Impact of Different Roll Sizes on Roller Compactor Granulations
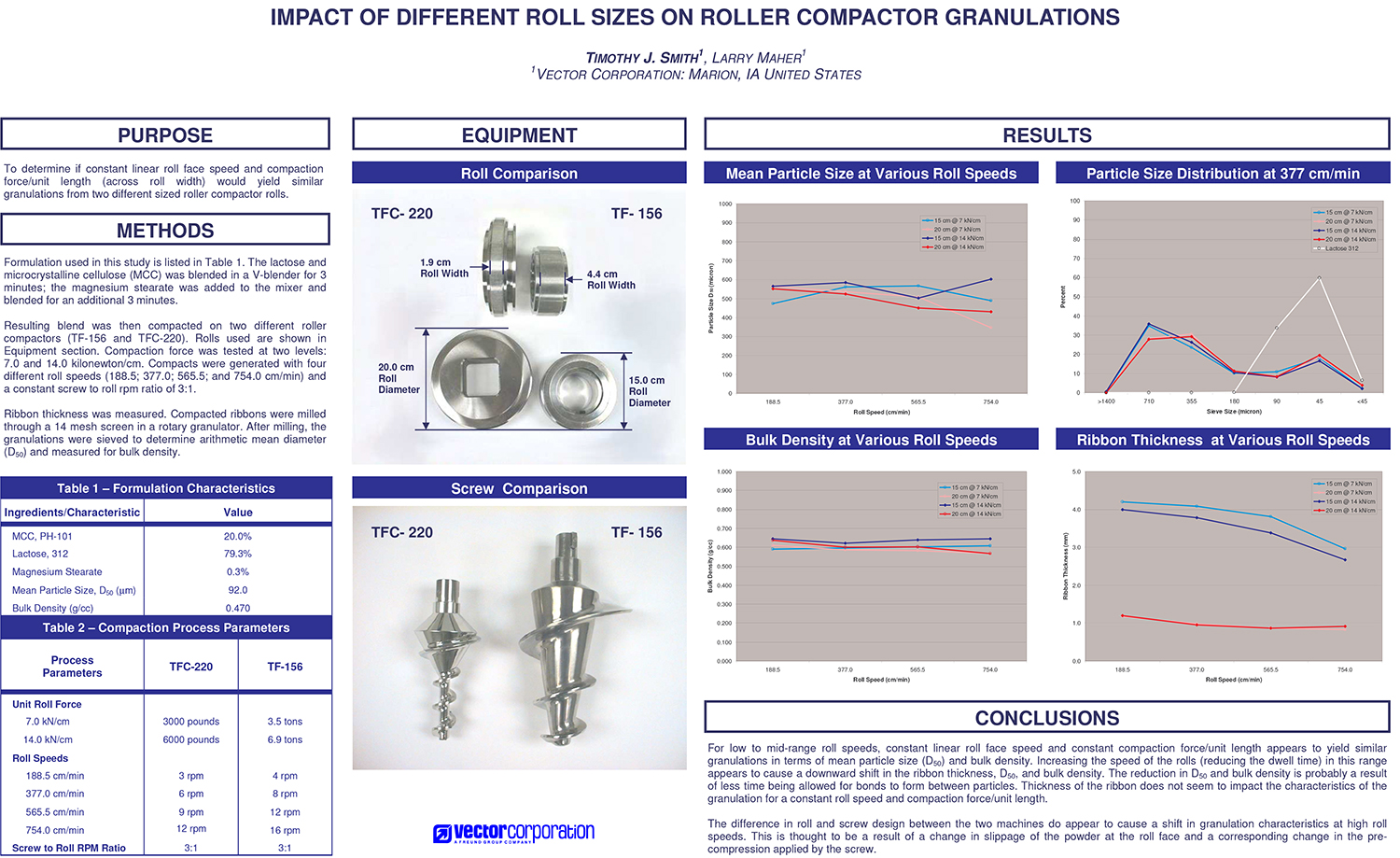
To determine if constant linear roll face speed and compaction force/unit length (across roll width) would yield similar granulations from two different sized roller compactor rolls.
To determine if constant linear roll face speed and compaction force/unit length (across roll width) would yield similar granulations from two different sized roller compactor rolls.
Fully perforated and partially perforated coating pans are commonly used for film coating processes. The aim of this study was to compare the coating processes using different types of perforation.
To compare the flow properties of granules prepared by top-drive and bottom-drive high-shear granulators.
To compare the results of particle size distribution and powder flowability determined by different methods.
To Compare Tablet Dissolution Profiles from Granulation made with both Top-Drive (TD) and Bottom-Drive (BD) High Shear Granulators.
To compare top-drive (TD) high shear granulation versus bottom-drive (BD) high-shear granulation.
To compare wet-granulations produced using top-drive (TD) and bottom-drive (BD) high-shear granulators.
To compare wet-granulation processes in a high-shear granulator and an innovative rotor processor.
To study the particle size changes that occur during the water infusion and high shear (or wet-mass) phases of a wet granulation process.
To determine the most effective end-point method for scale-up of wet granulations using the following methods: 1) Wet-mass time (WMT) 2) Product temperature change (DT) 3) Peak power consumption (KWp)
To incorporate wet-mass, or high shear, mixer blade power consumption information.
High-shear mixers are commonly used in the production of wet granulations. These granulations can be used for both immediate and controlled release dosage forms. Occasionally it is necessary to modify the batch size to meet production requirements. This study was done to determine the effect of product load volume in a high-shear granulation process using both immediate and controlled release formulations.
To determine the effect of consecutive multi-batch high-shear granulation processing on: 1) particle size and 2) thermal processing characteristics