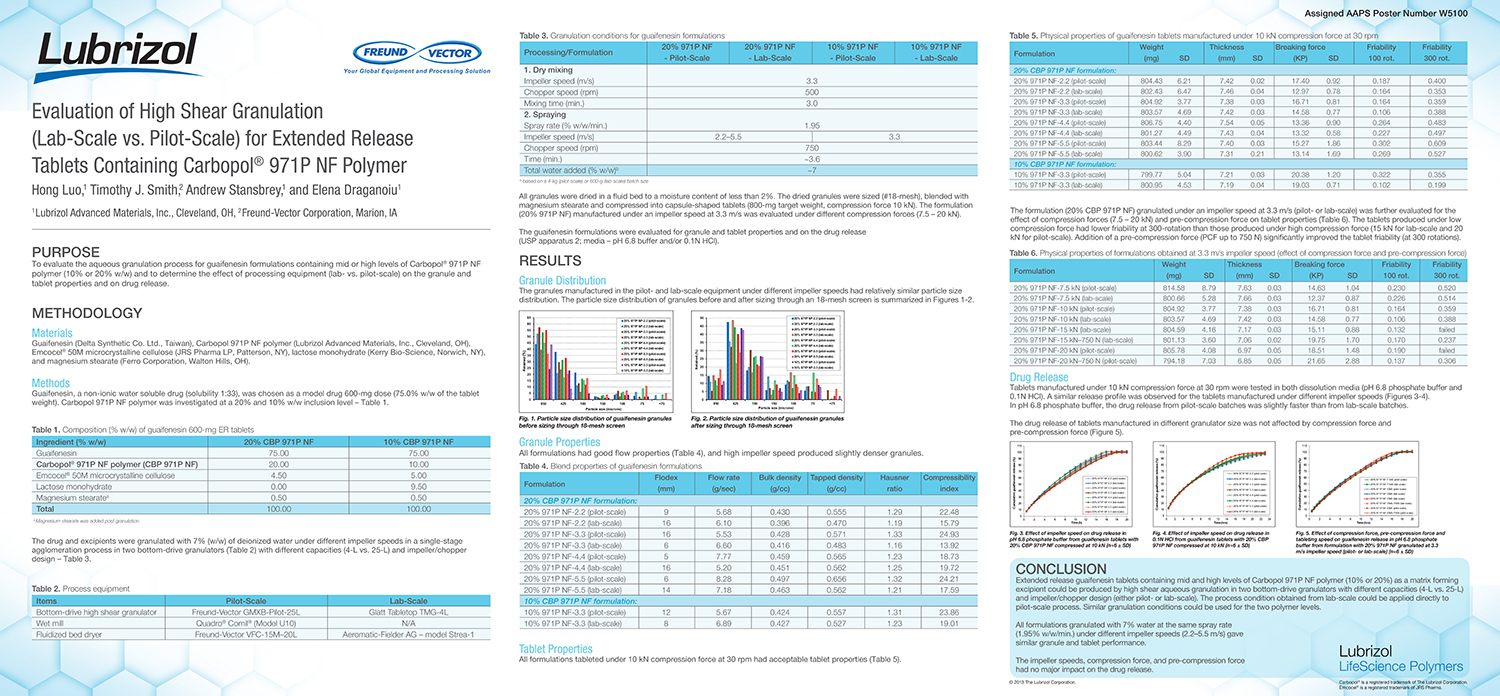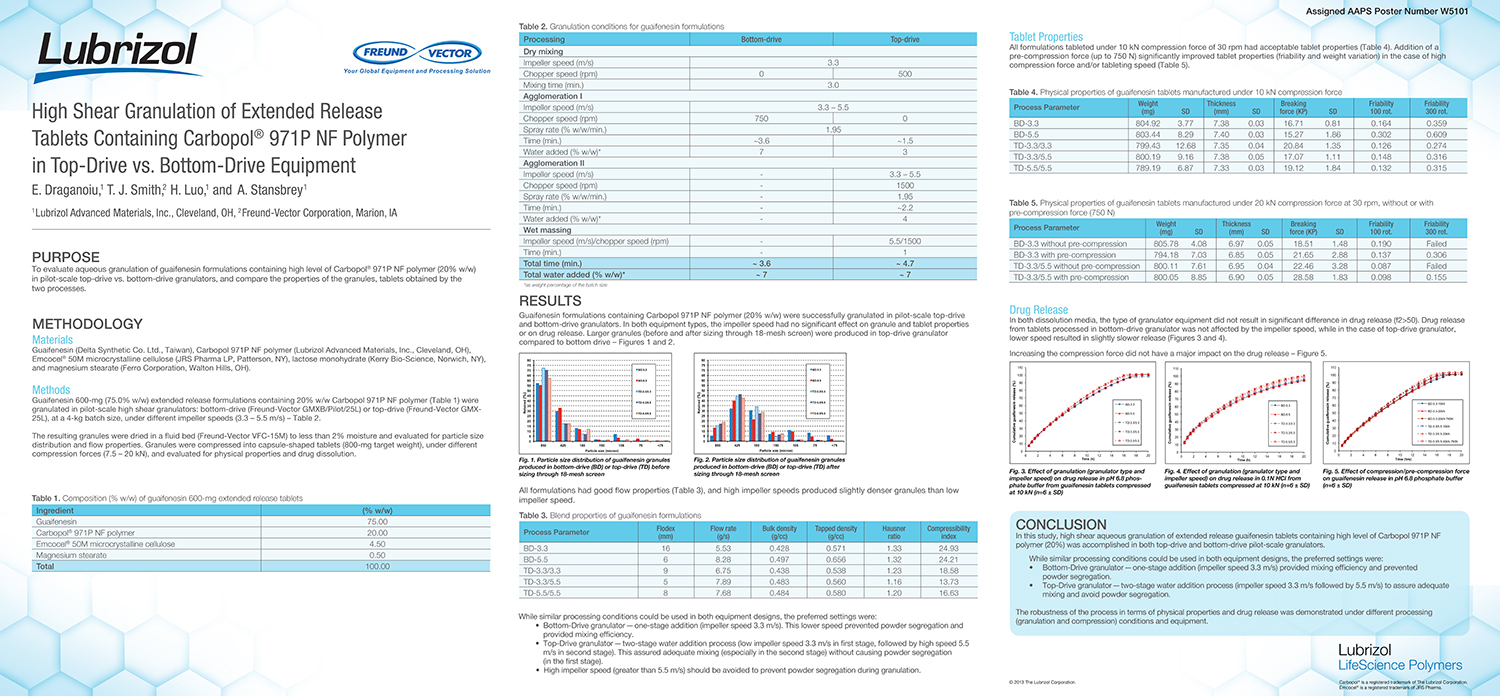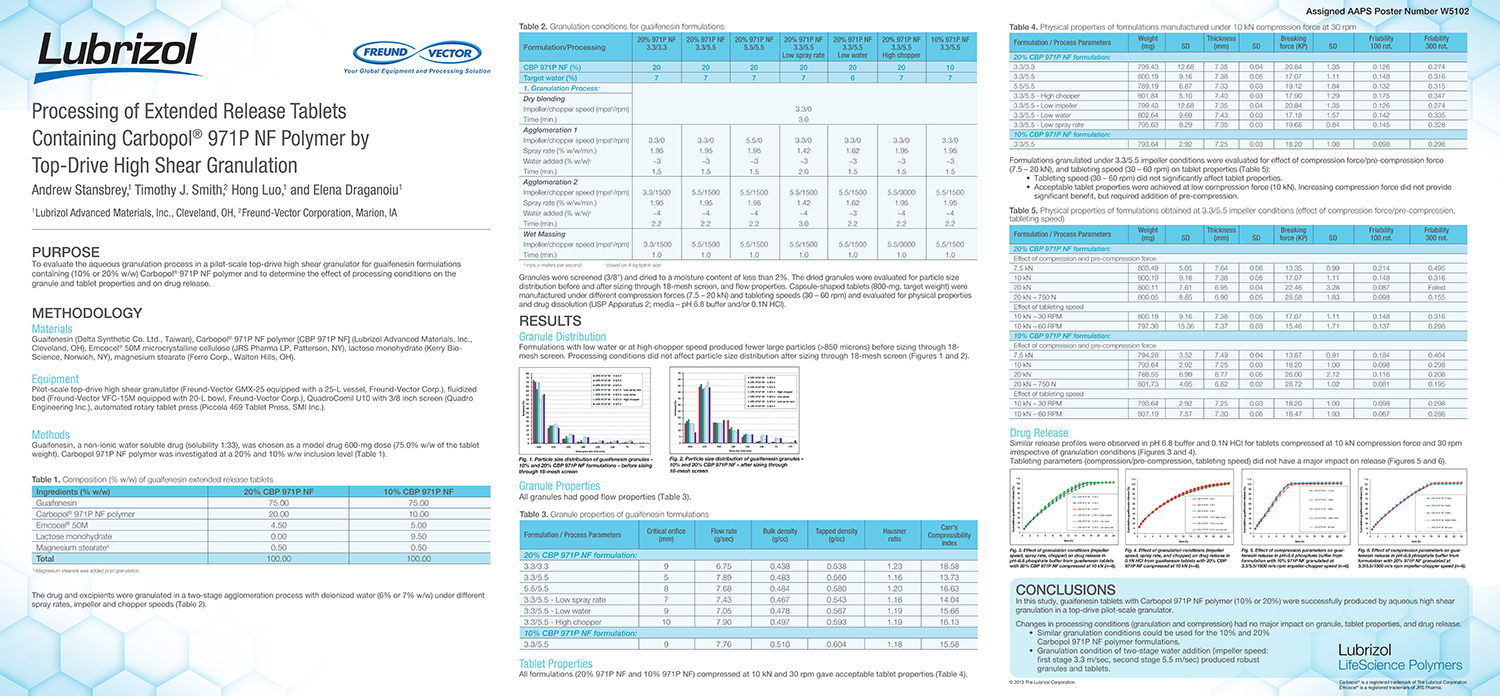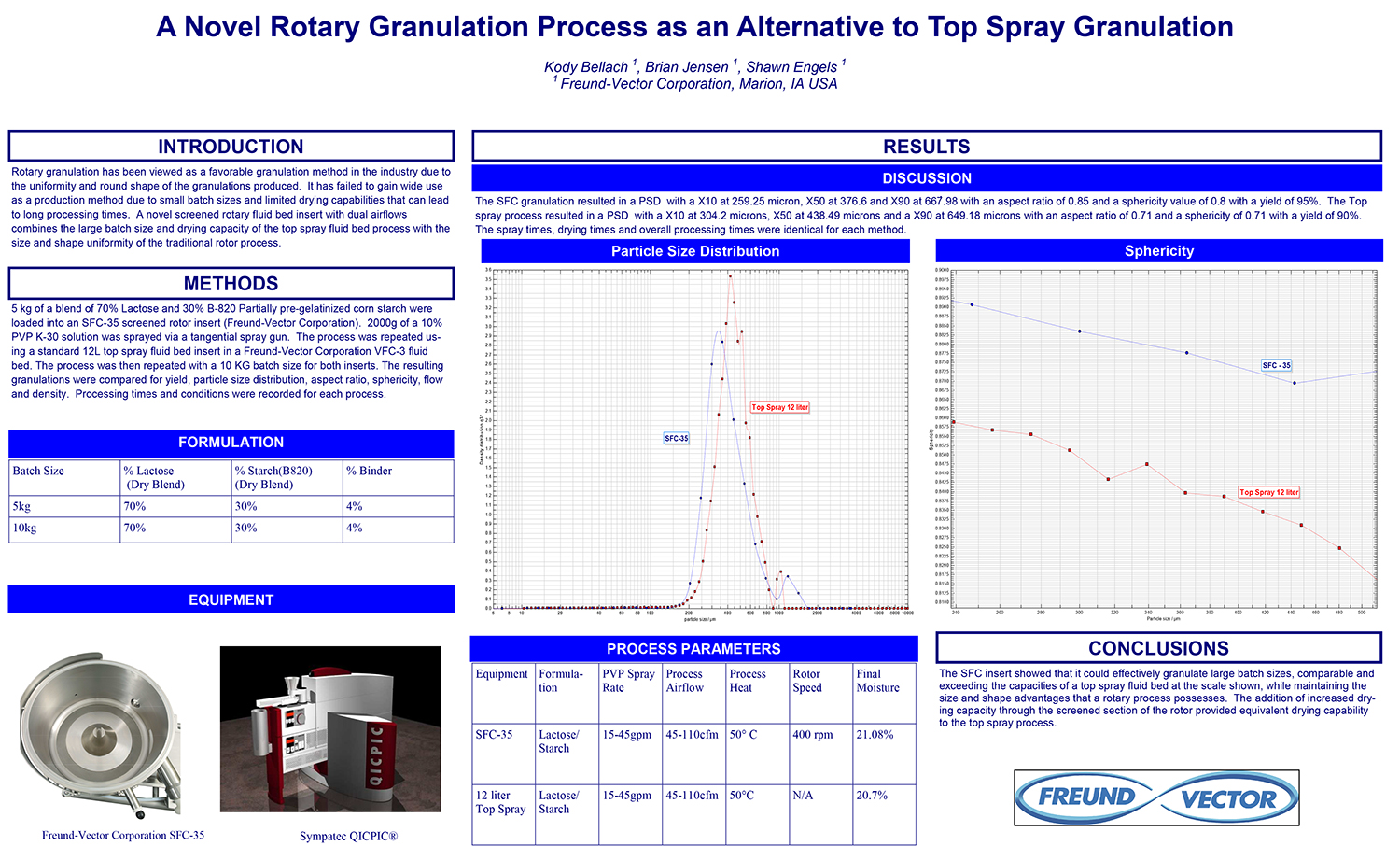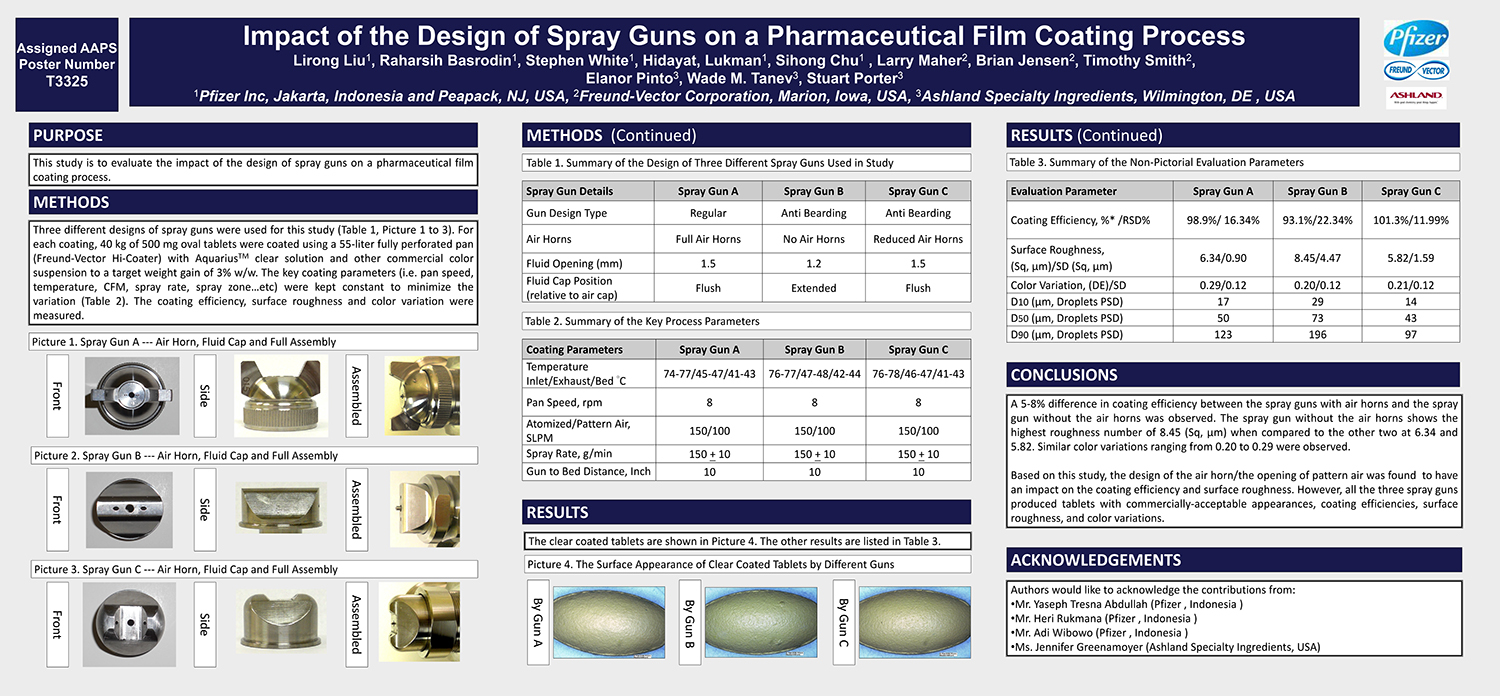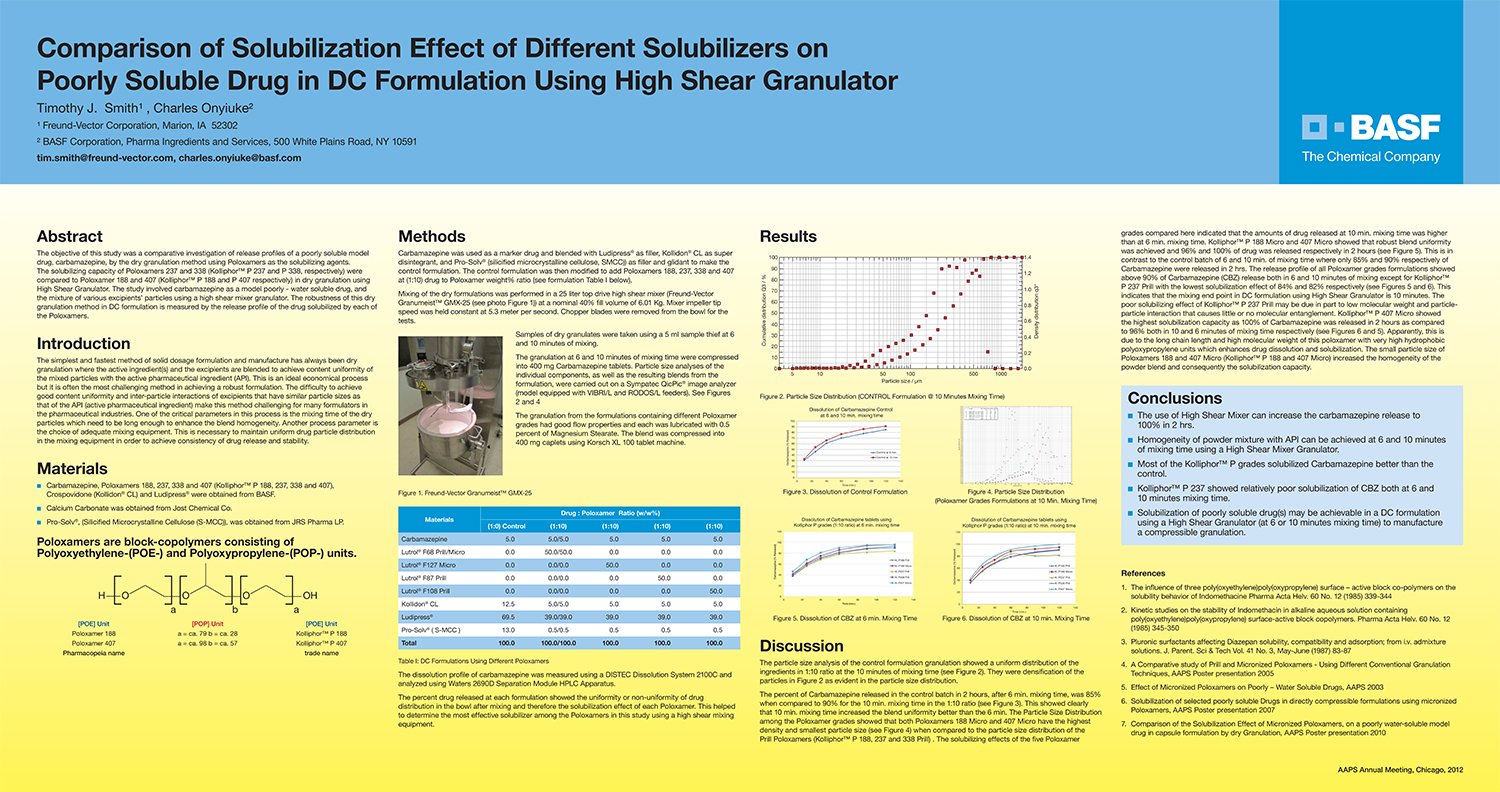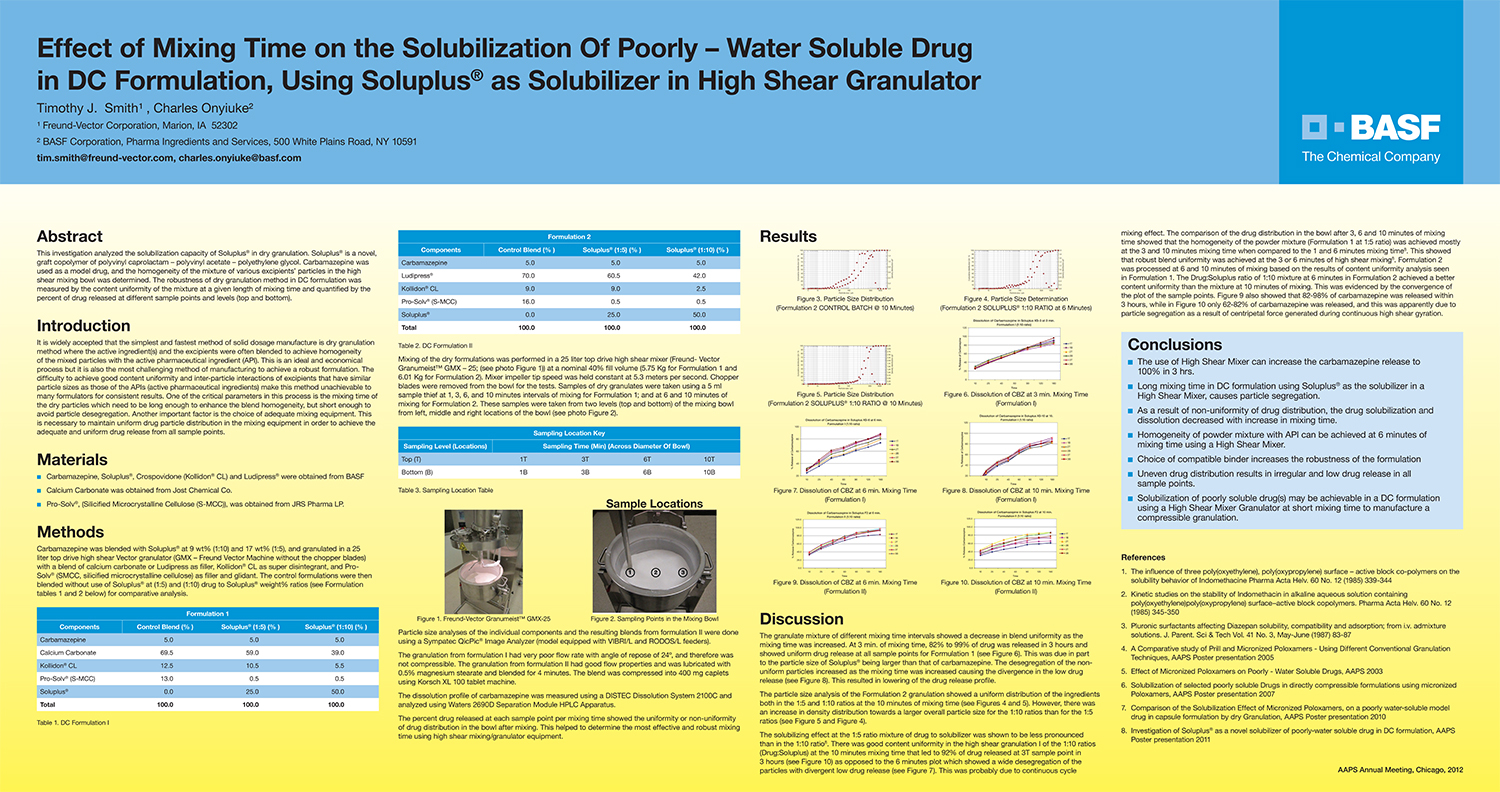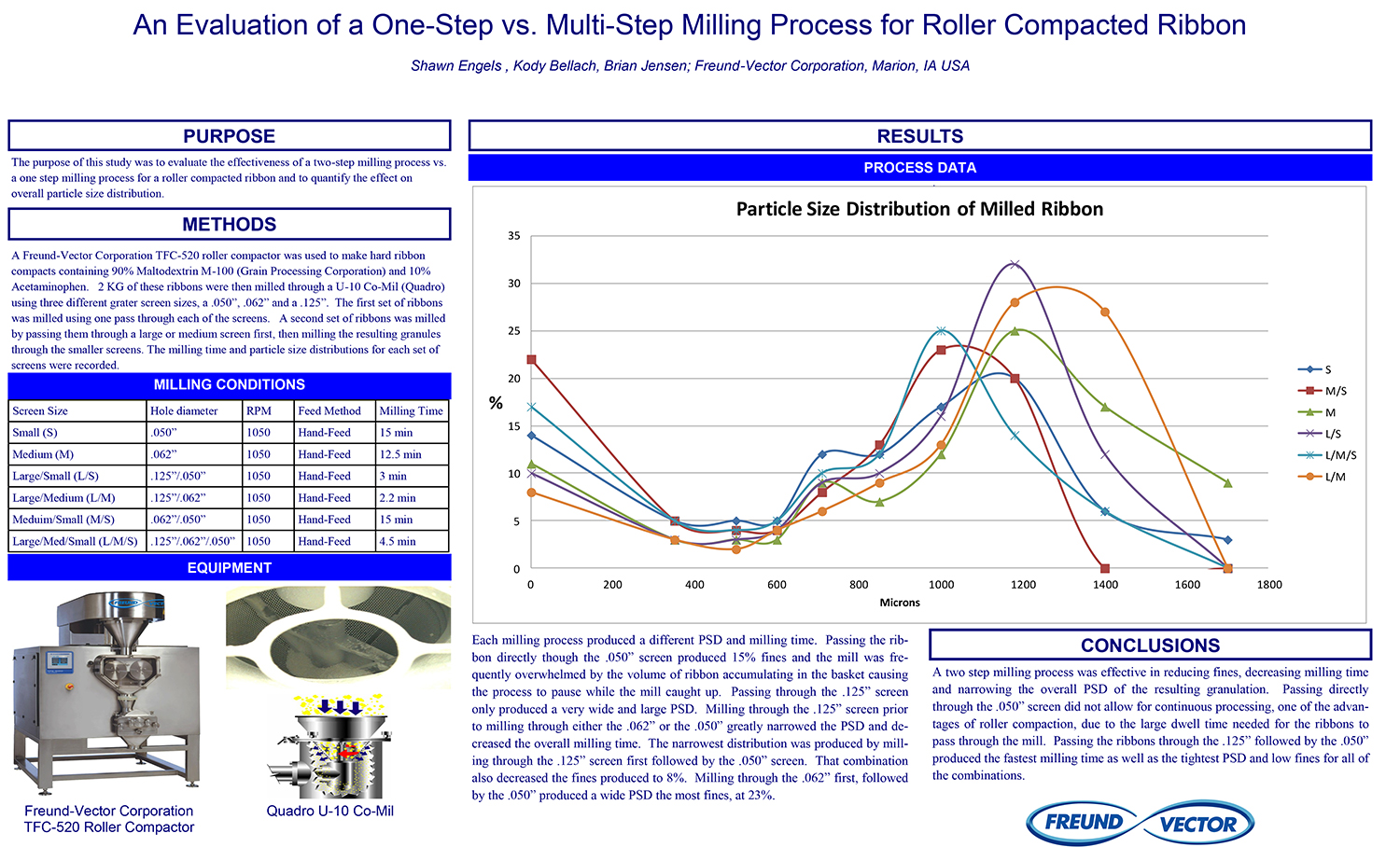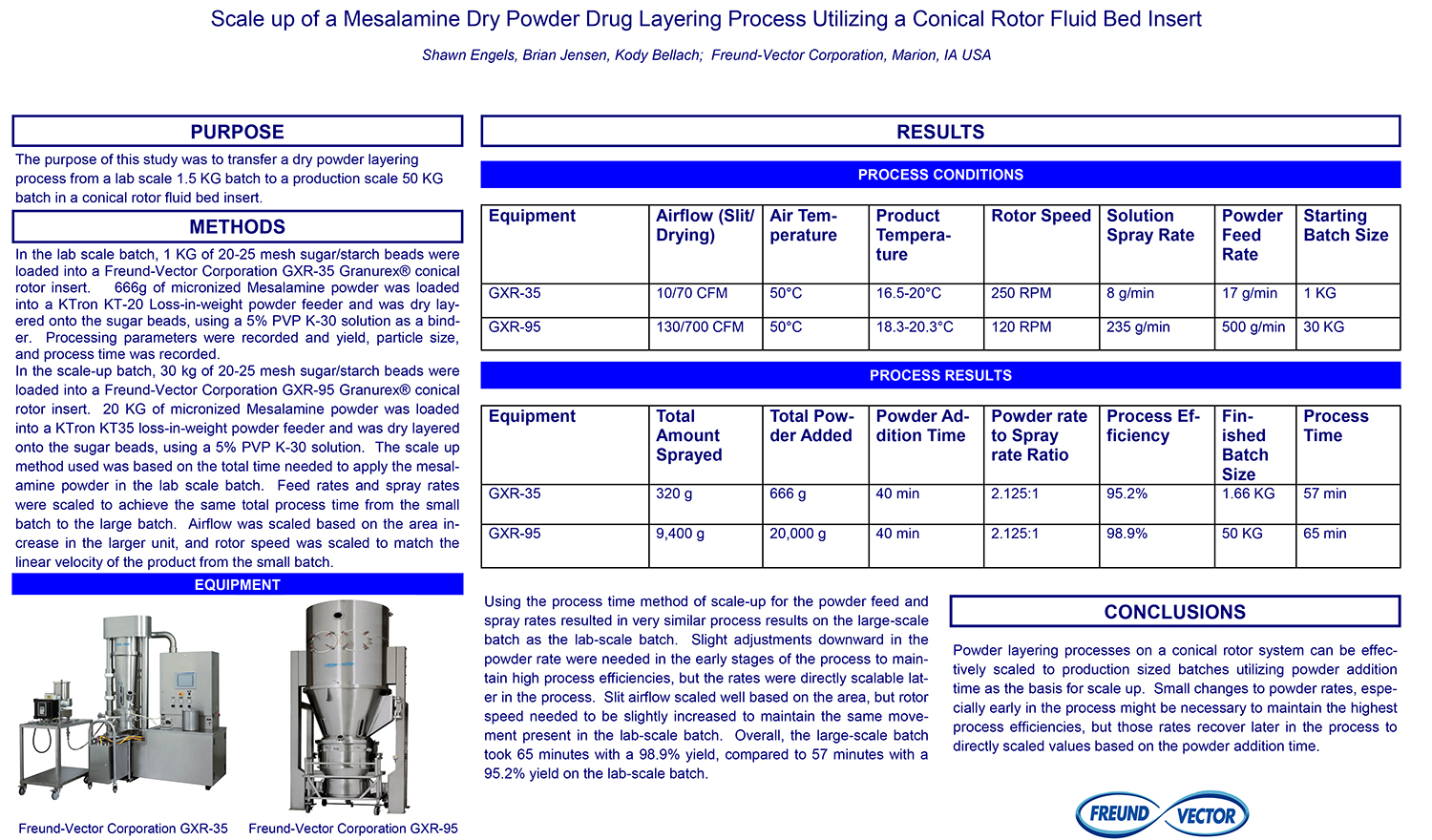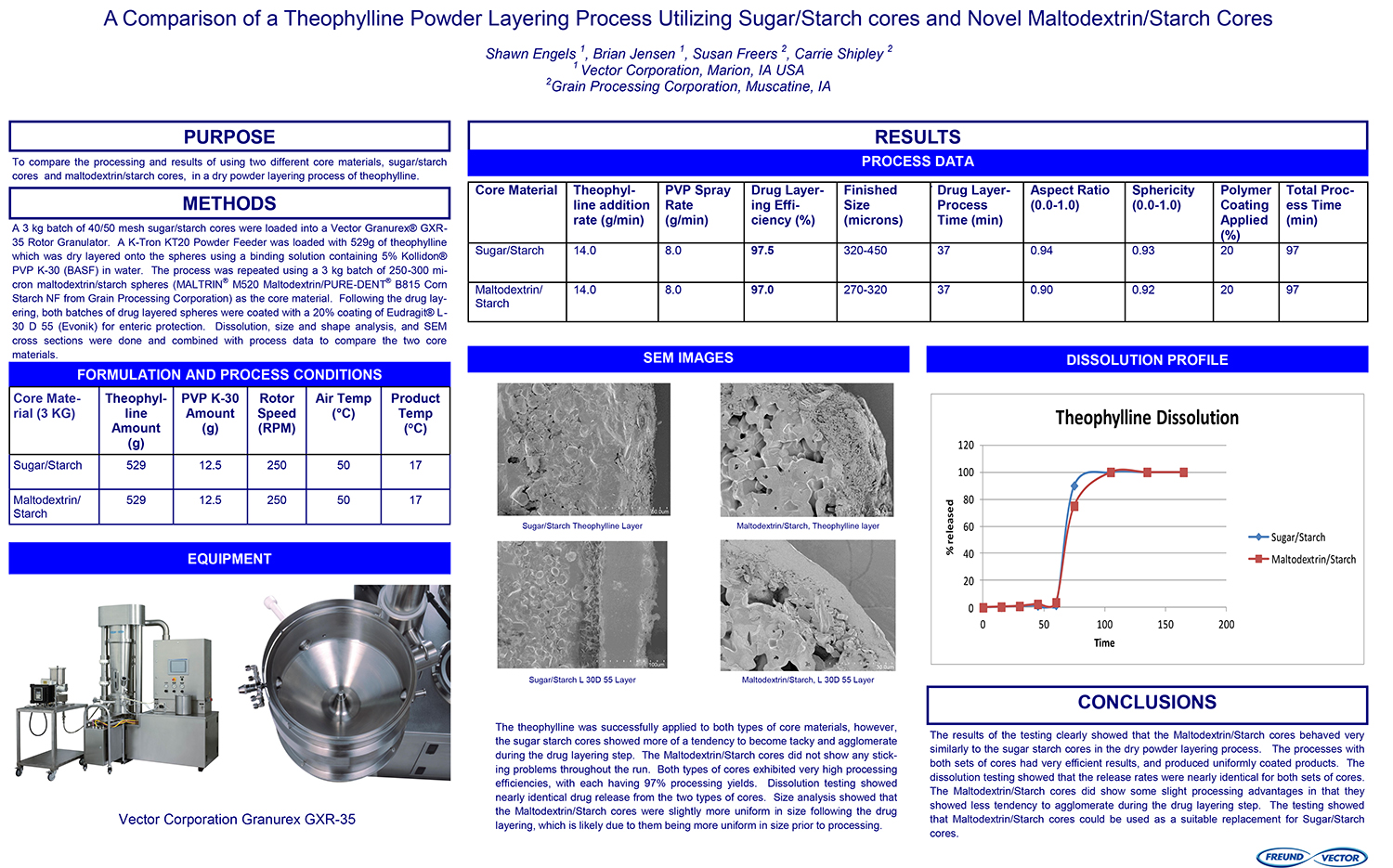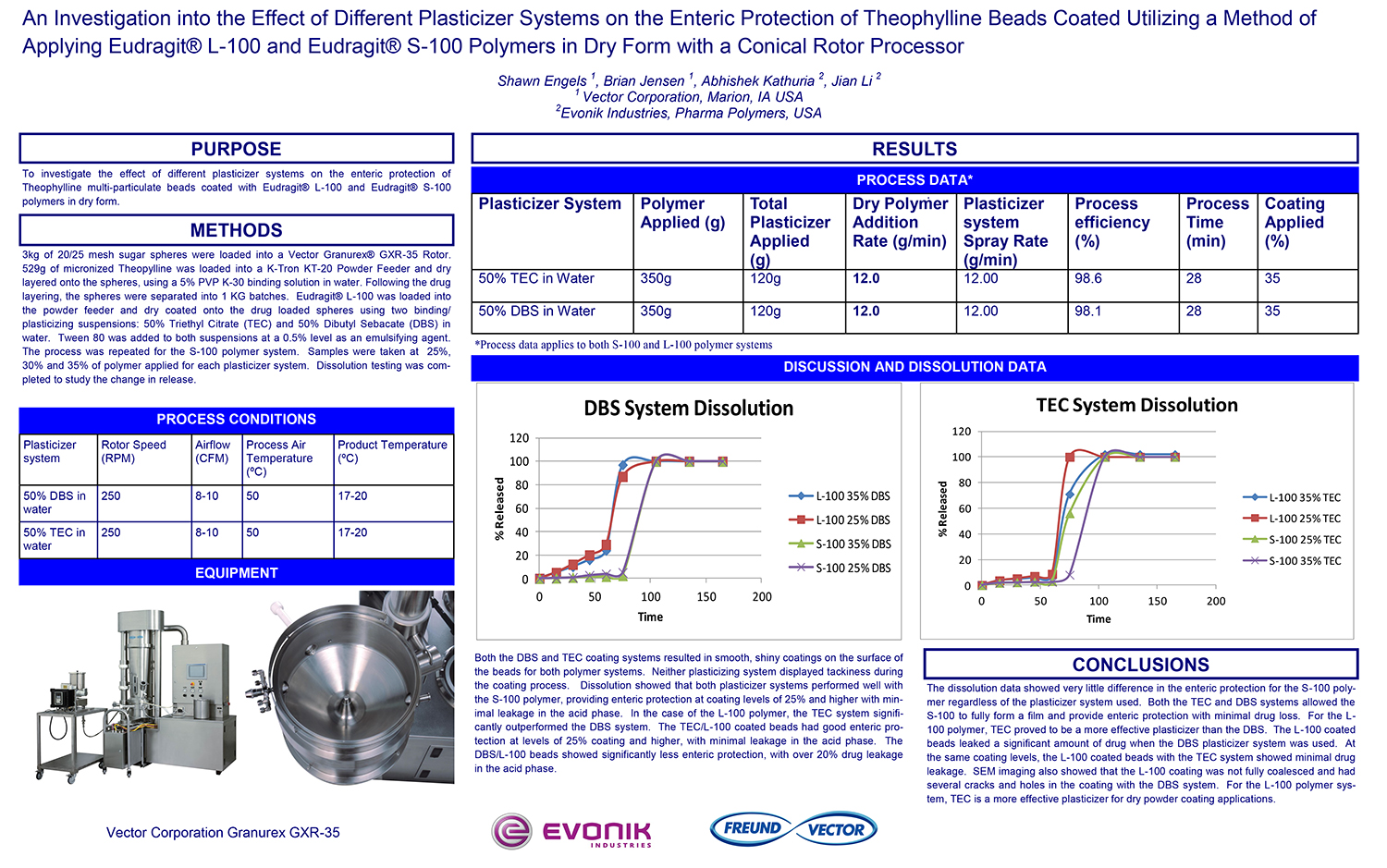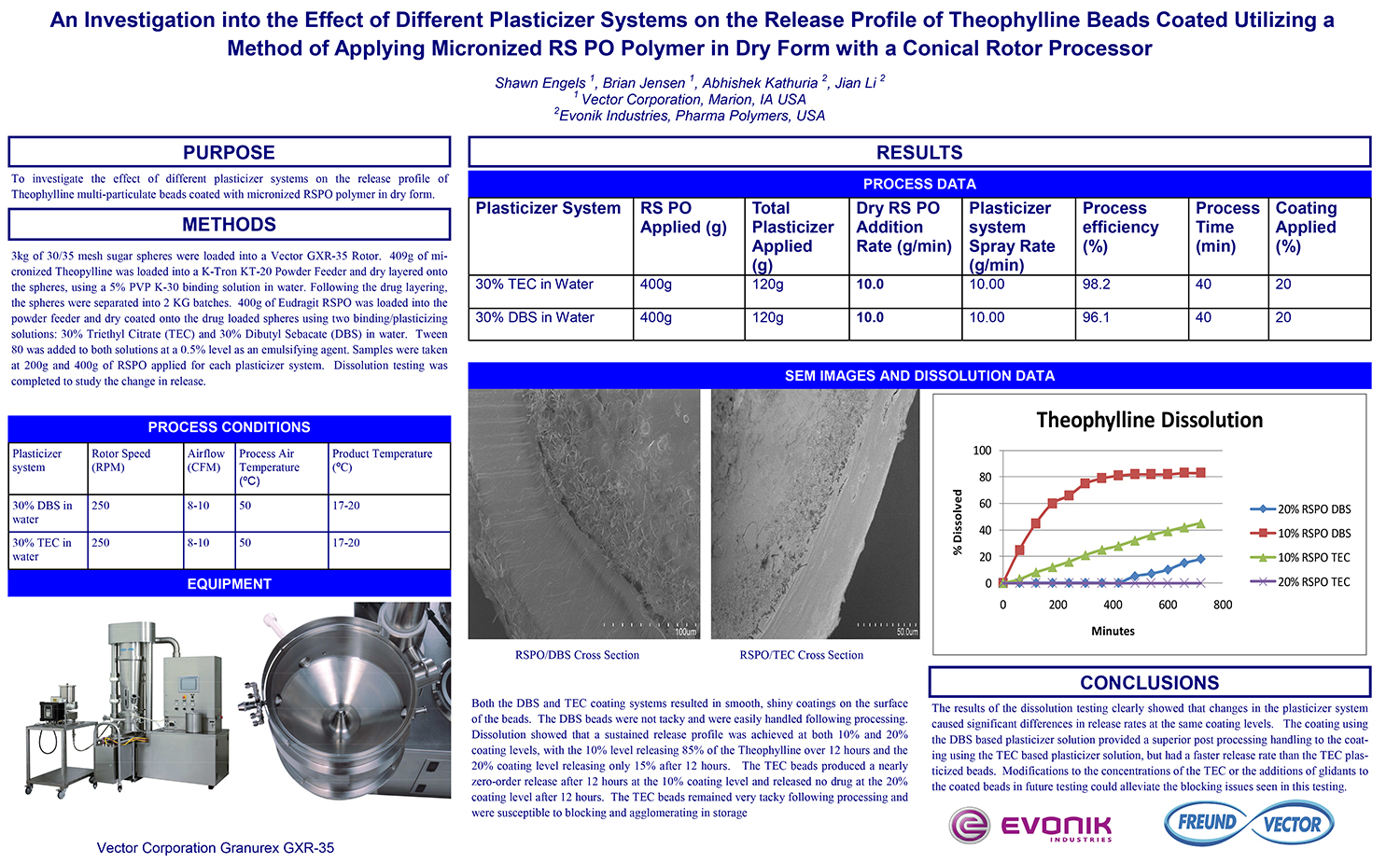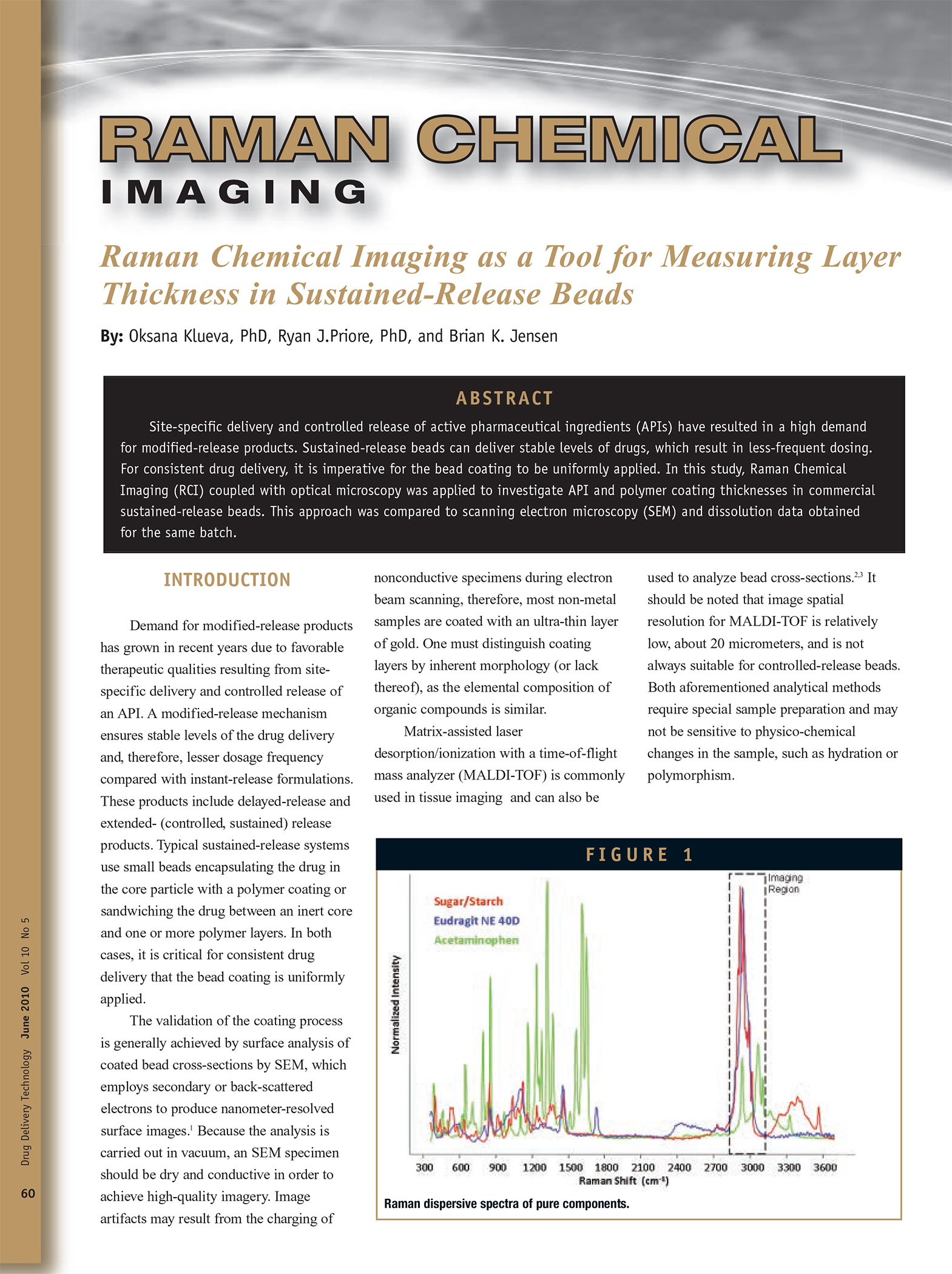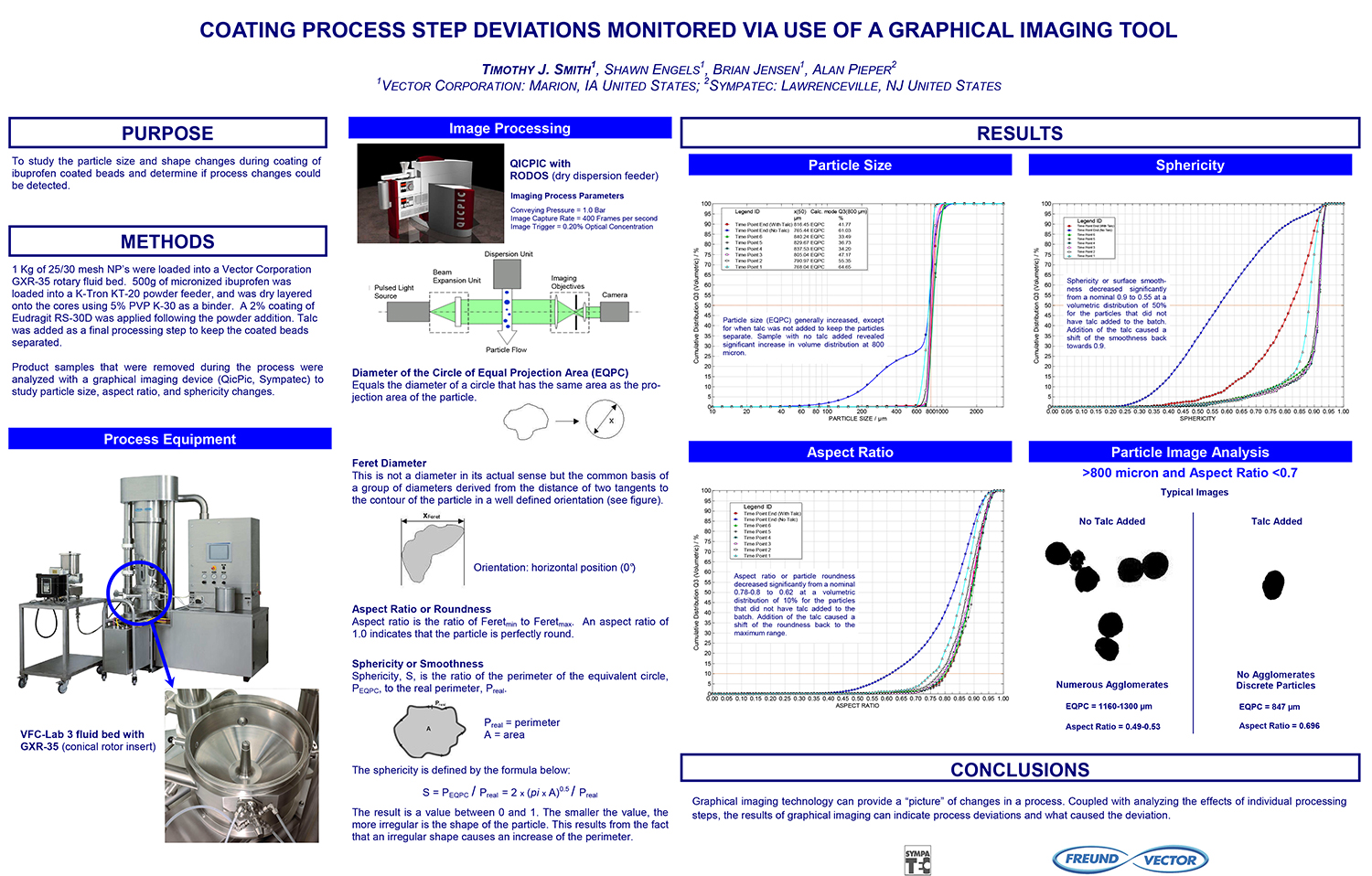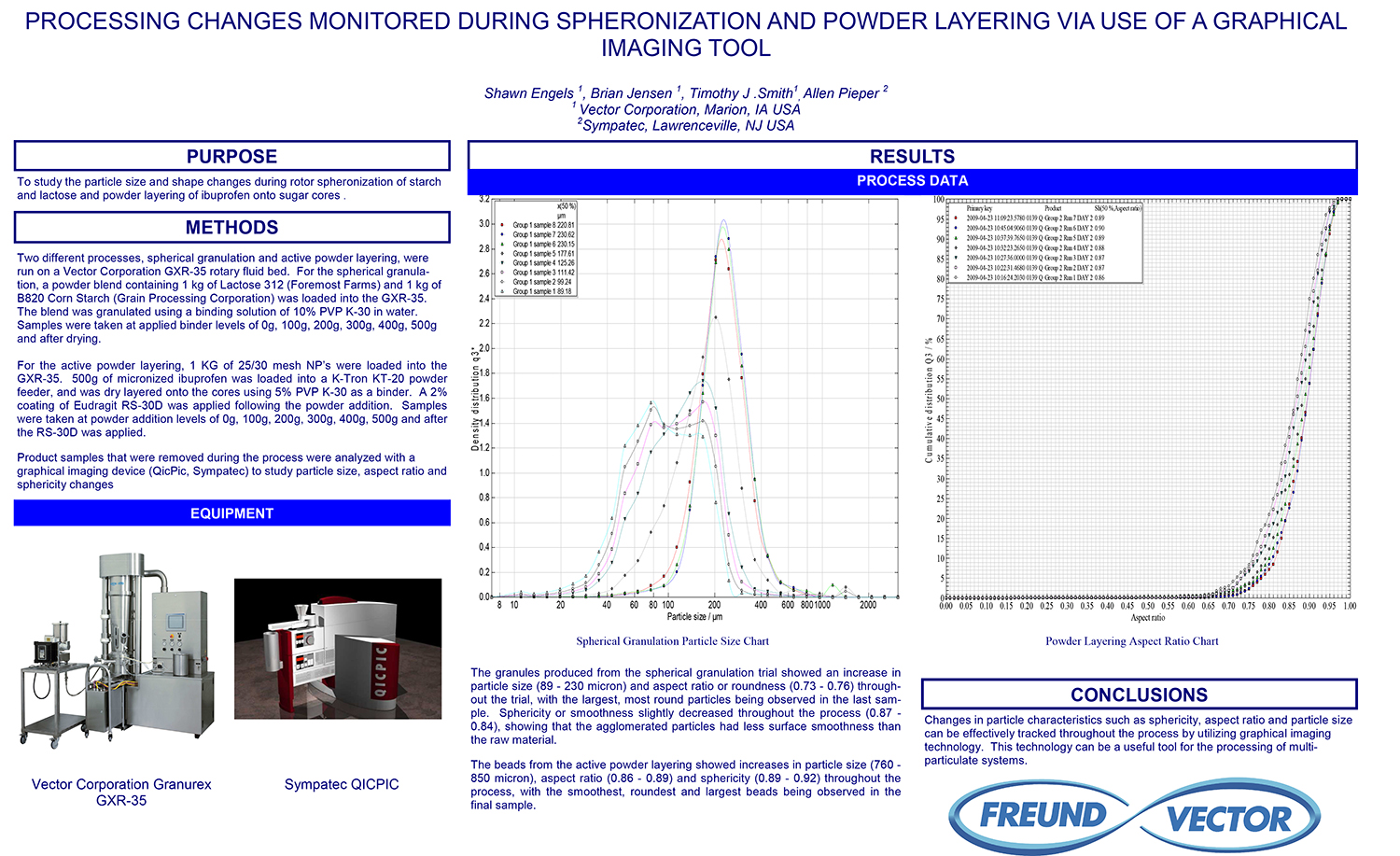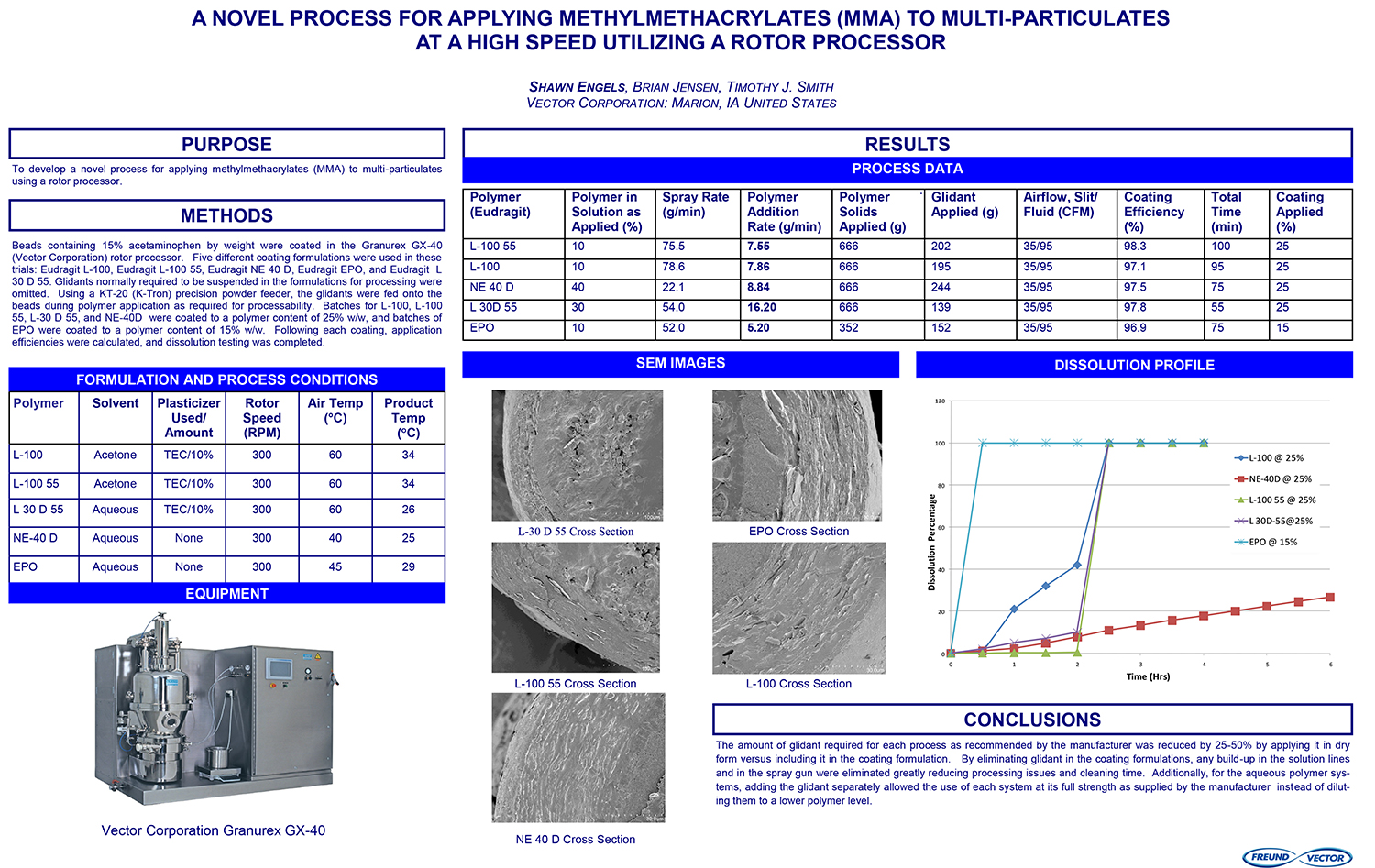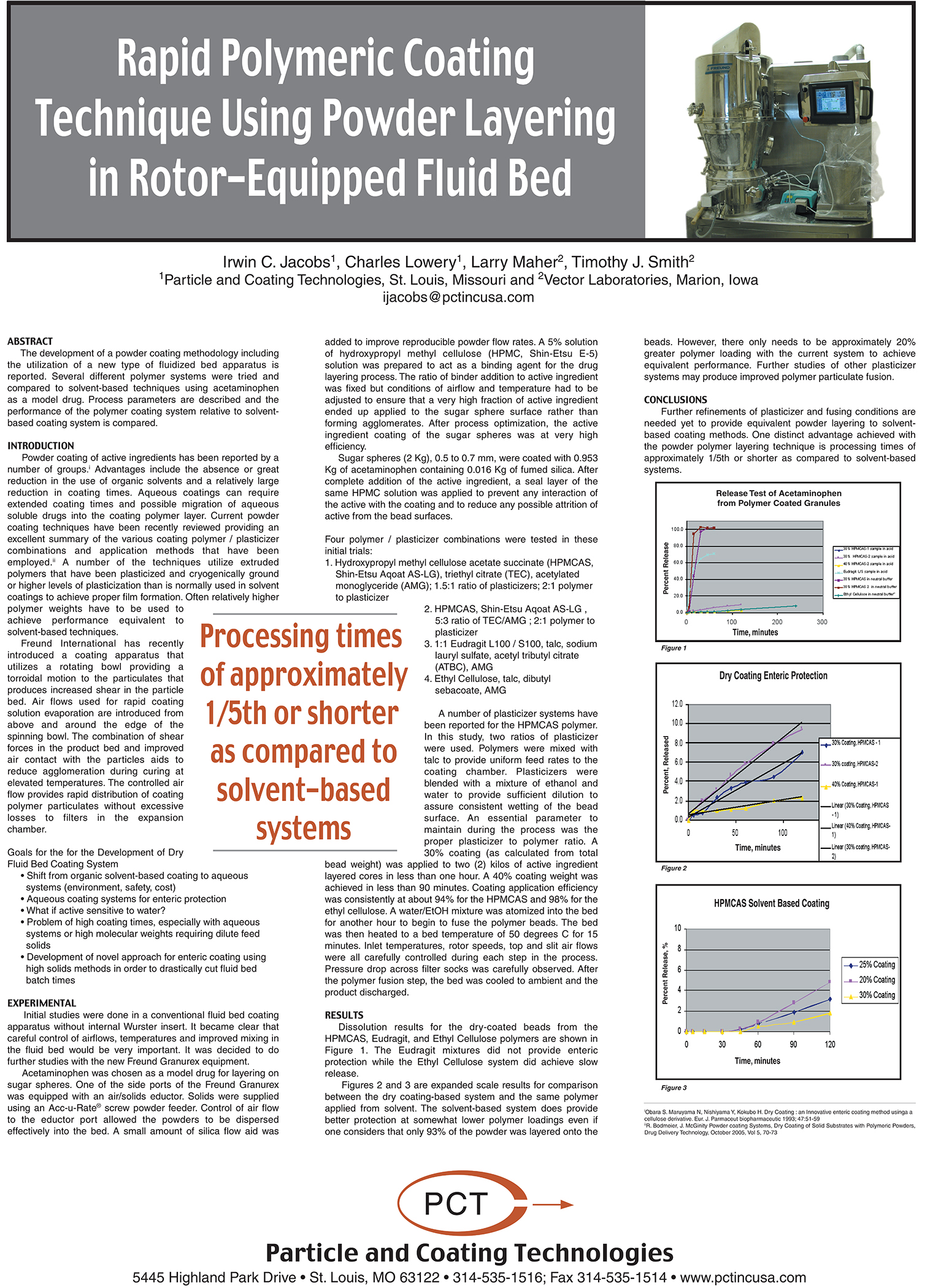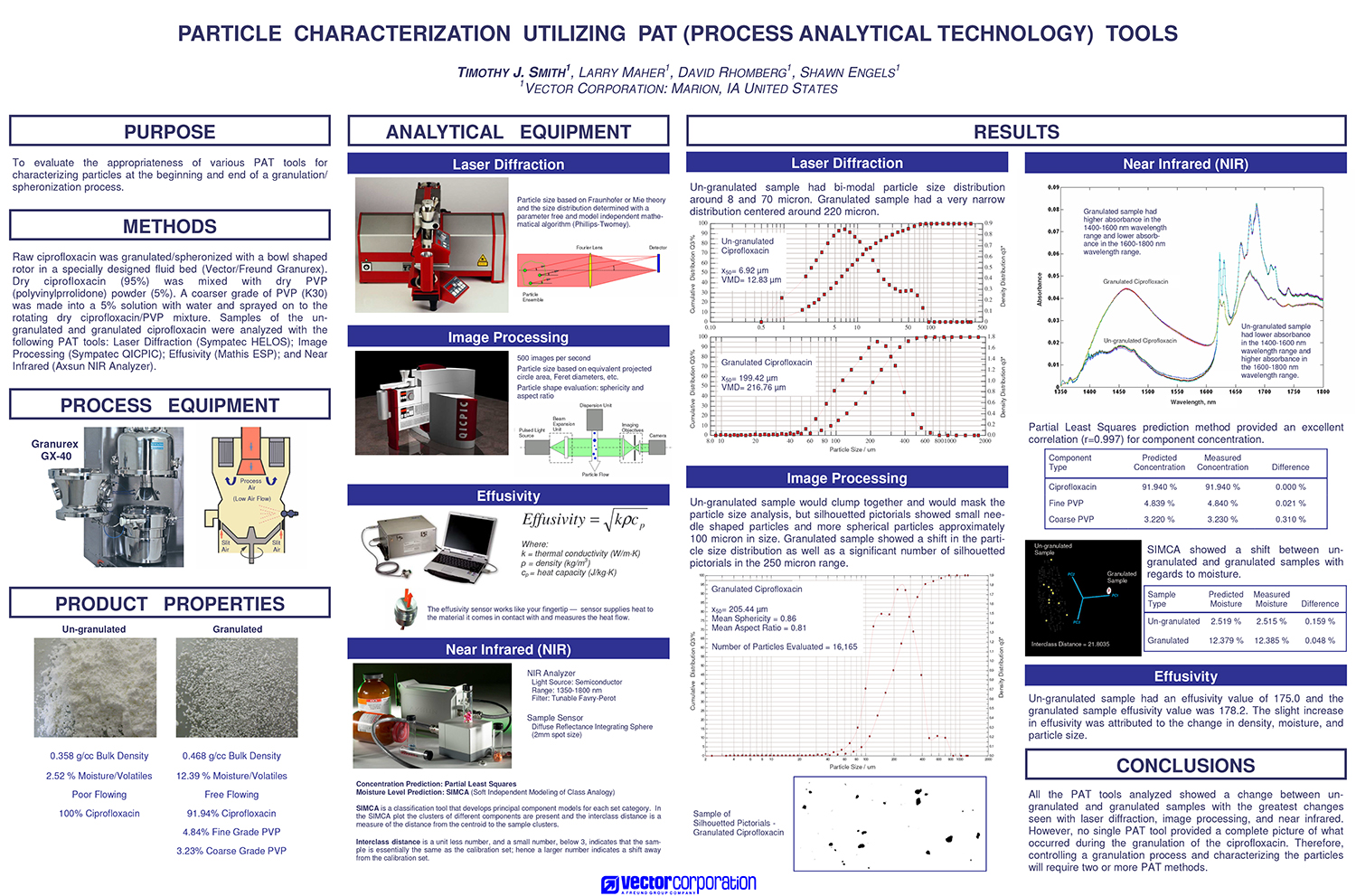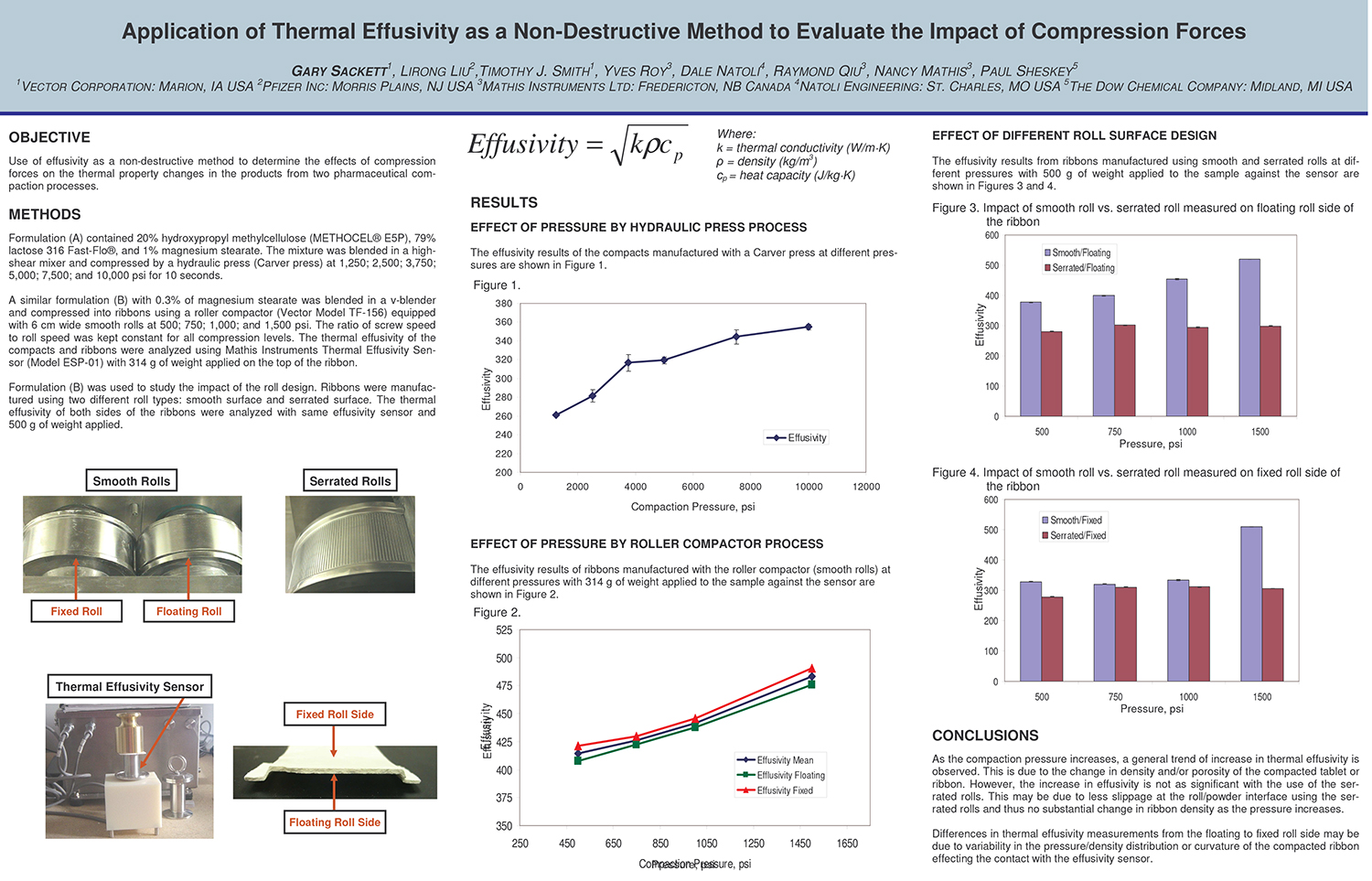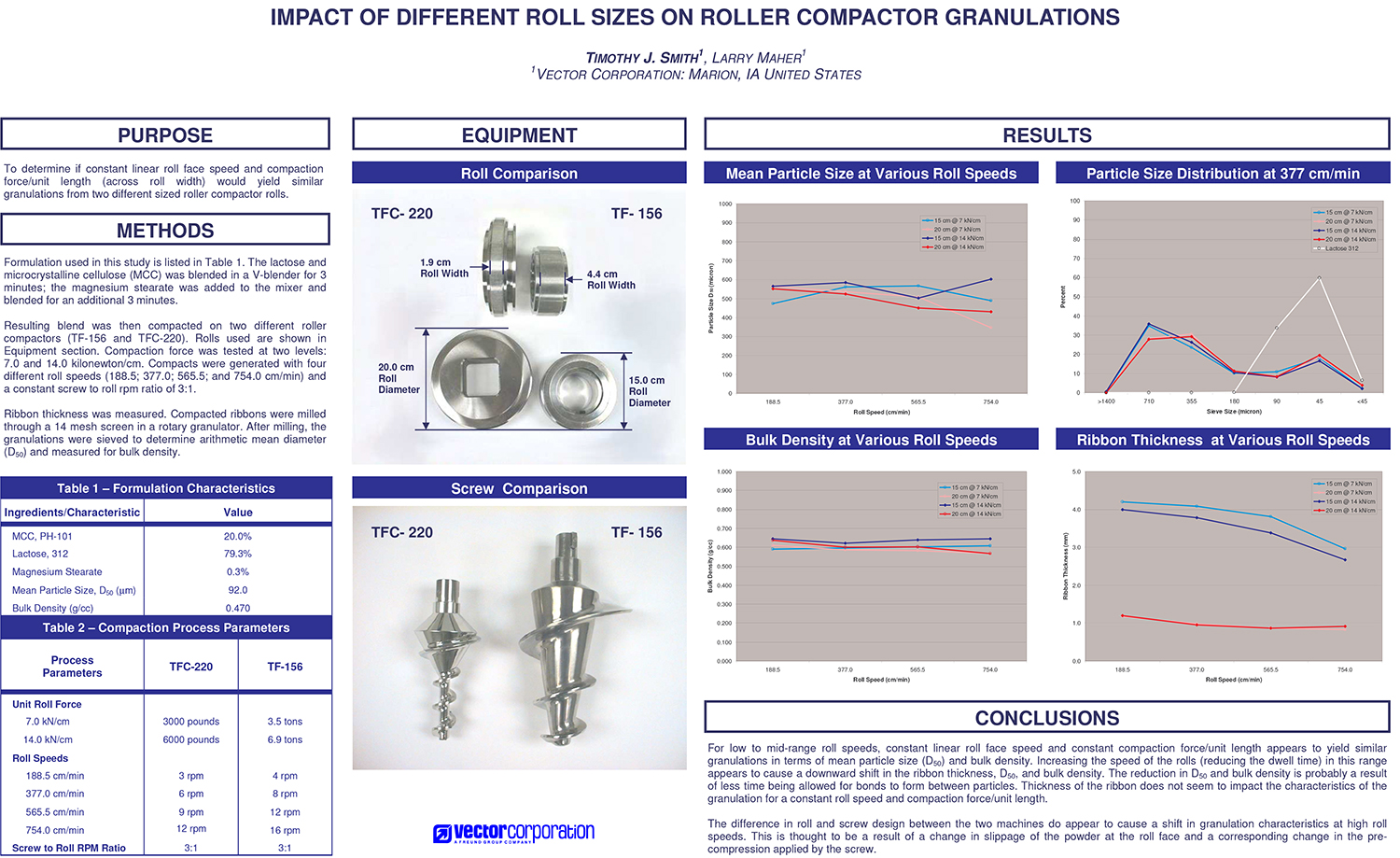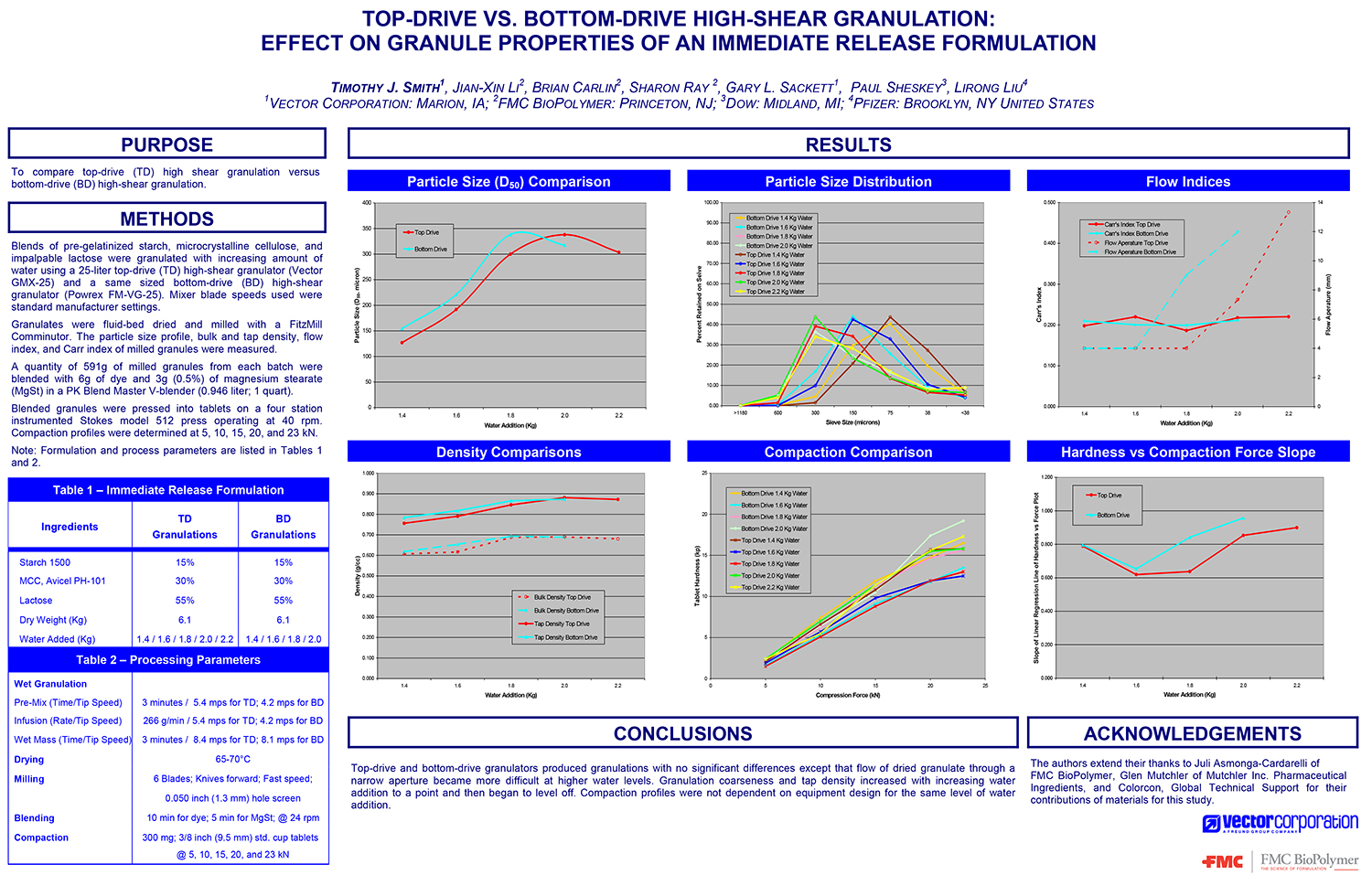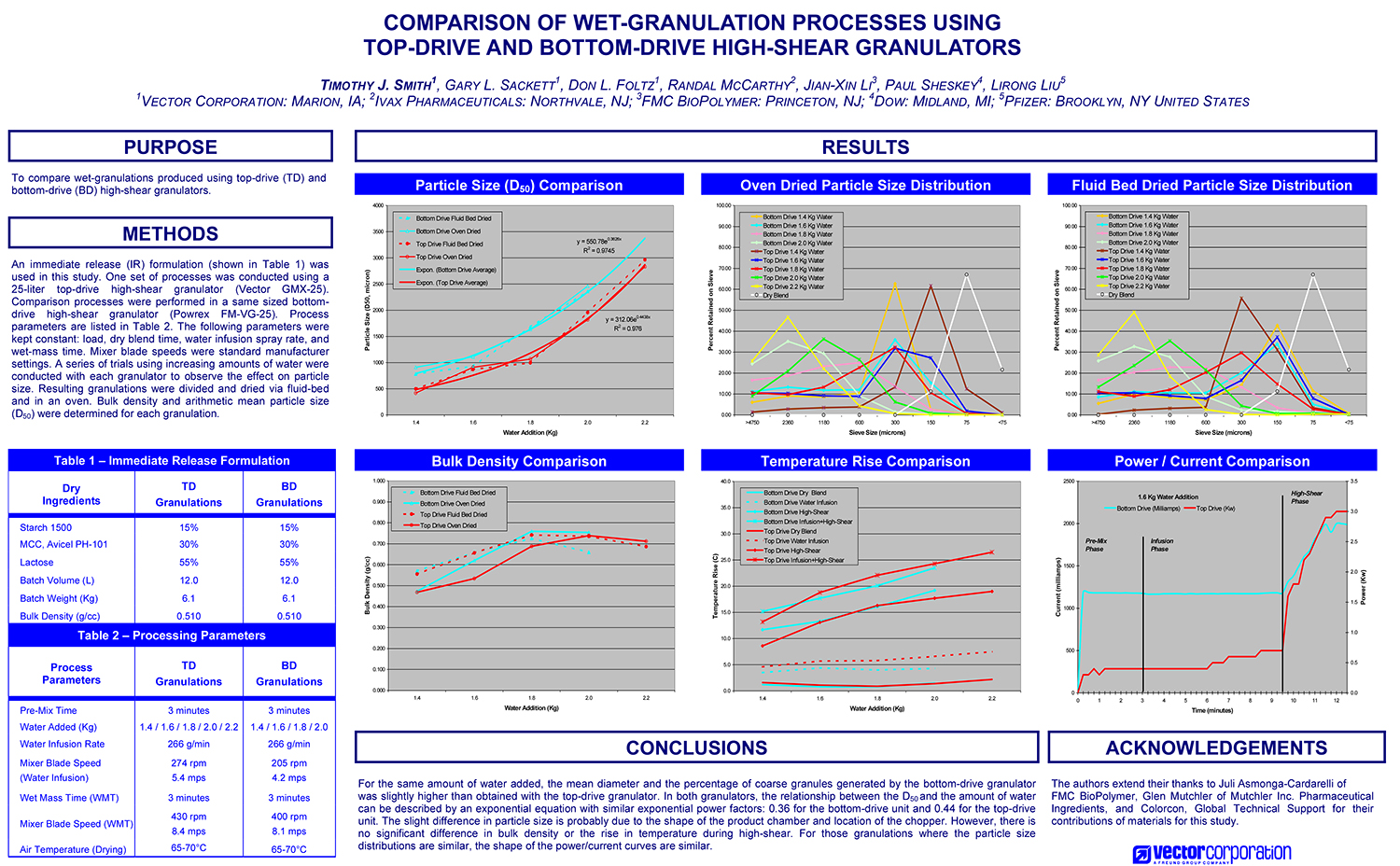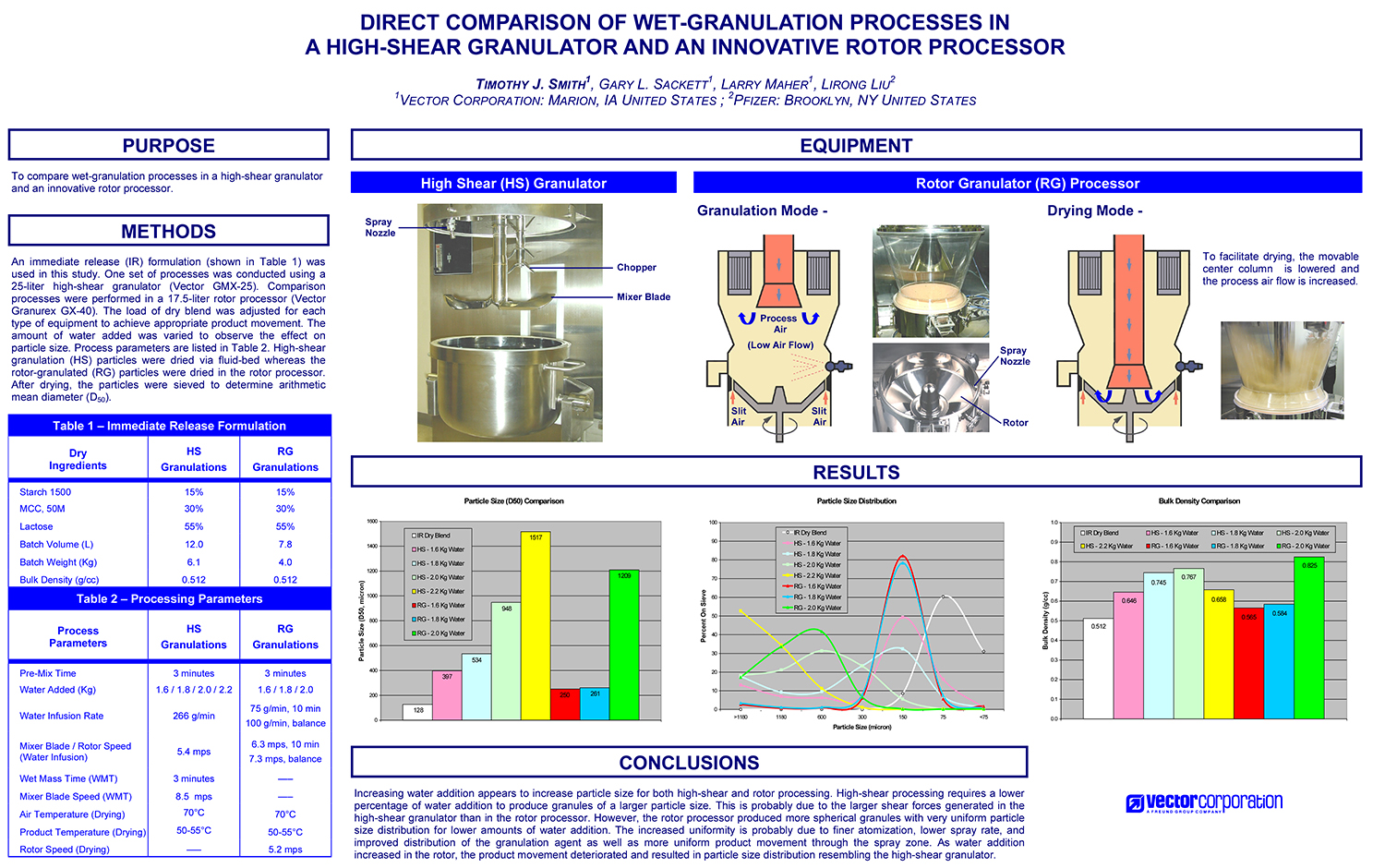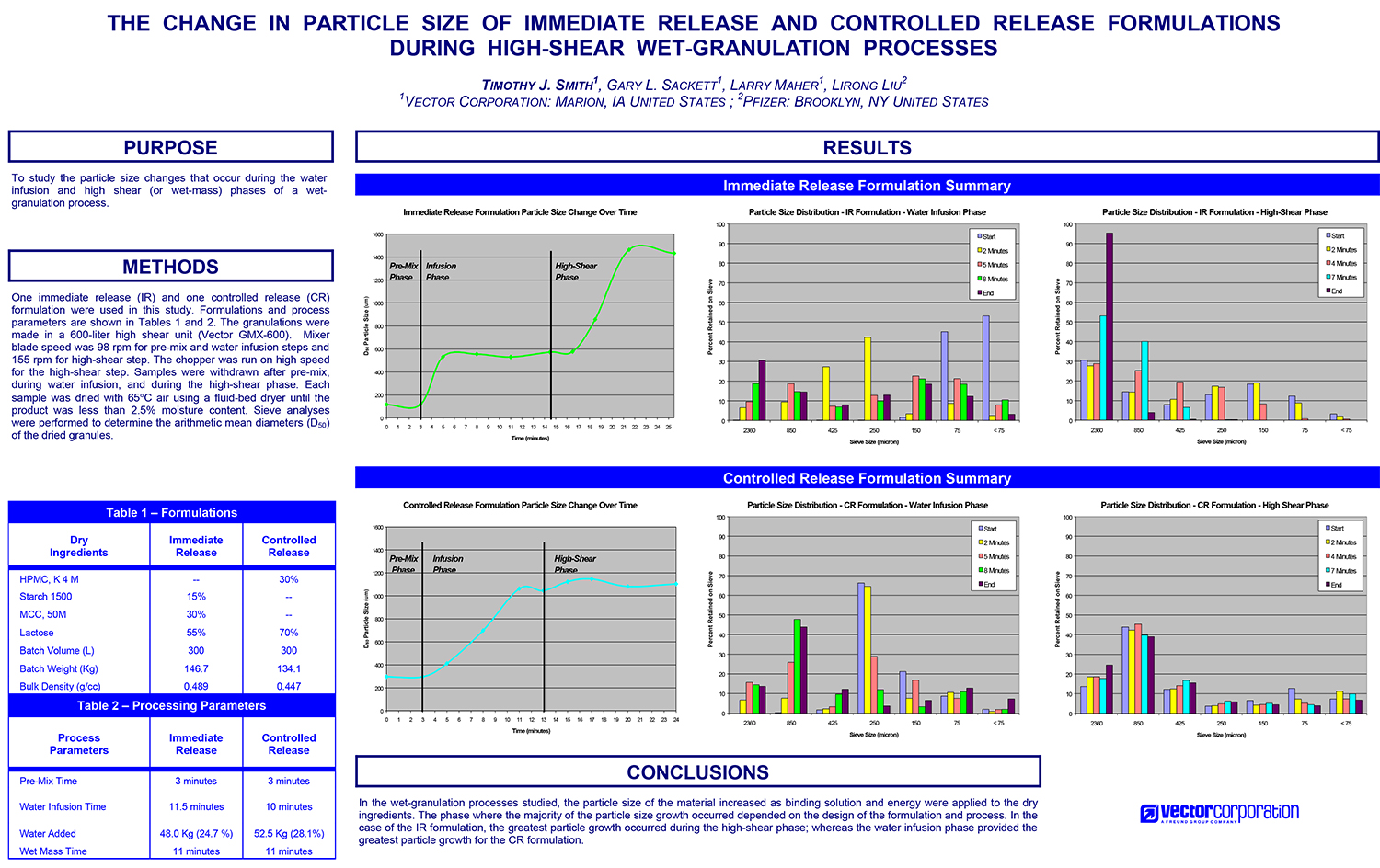
A Comparison of Content Uniformity and Dissolution of API Applied to Different Spherical Core Materials using a Controlled Release Drug Layering Process
To investigate the process of dry powder drug layering and enteric coating on three spherical core materials: two traditional cores, sugar/starch and microcrystalline cellulose, and a newer type of core manufactured from starch and maltodextrin. To compare dissolution and content uniformity for the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) applied at different percentages on powder layered cores and enteric coated finished spheres.